Glossary
The English version of our glossary is currently under construction and will be regularly updated.
- A(31)
- B(17)
- C(44)
- D(20)
- E(30)
- F(18)
- G(15)
- H(10)
- I(27)
- J
- K(4)
- L(9)
- M(16)
- N(6)
- O(13)
- P(36)
- Q
- R(14)
- S(45)
- T(23)
- U(5)
- V
- W(3)
- X
- Y(1)
- Z(1)
- 0(2)
Macronutrients
Inorganic chemical compounds that algae ingest in large quantities and require in order to produce biomass.
moreMarginal sea
In oceanography, a marginal sea is a secondary sea that, unlike mediterranean seas, is situated on the edge of the mainland and is separated from the open ocean by archipelagos or peninsulas. Examples include the Bering Sea, North Sea, and Sea of Japan.
moreMass balance (of glaciers, ice caps or ice sheets)
In glaciology, the difference between a body of ice’s mass gain and mass loss is referred to as its mass balance.
moreMass-balance buoy
Autonomous measuring system that uses acoustic methods to determine sea-ice and snow thickness.
more
Meiofauna
Refers to a group of small animals – as a rule, between 0.3 and 1 mm in diameter – that chiefly live in marine sediments but can also be found in terrestrial habitats. In terms of size, they lie between the microfauna and macrofauna.
moreMelt pond
Every summer, the snow cover on Arctic sea ice melts completely, leaving behind ponds of meltwater.
more
Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC)
This global “conveyor belt” redistributes massive amounts of heat, salt, nutrients and gases among all oceans.
more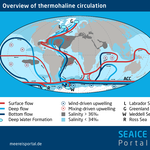
Metazoans
Multicellular, heterotrophic organisms belonging to the animal kingdom. Unlike single-celled organisms like protozoans, metazoans are composed of multiple cells, which are subdivided into specialised tissues and organs capable of performing a range of functions.
moreMethan (CH₄)
Gaseous hydrocarbon.
moreMicrowaves
A type of electromagnetic wave.
moreMid-ocean ridge
An extensive underwater mountain range that can in some cases include individual islands above sea level.
moreMilanković cycles
Model used to explain the occurrence of glacial and interglacial periods by means of quasi-periodic variations in Earth’s orbit, which result in changed exposure to solar radiation.
moreMixotrophic protist
Single-celled or multicellular eukaryotic lifeform (microorganism) that can use a mix of organic / inorganic sources of carbon, i.e., can also use photosynthesis.
moreMixotrophy
Mixotrophs are those organisms that can use a mix of organic / inorganic sources of carbon, i.e., can also use photosynthesis.
moreMontreal Protocol
Regulates the consumption and production of chemicals containing chlorine or bromine, which can destroy stratospheric ozone.
moreMultiyear ice
Old ice that is at least two metres thick and has survived at least two summers.
more