Glossary
The English version of our glossary is currently under construction and will be regularly updated.
- A(31)
- B(17)
- C(44)
- D(20)
- E(30)
- F(18)
- G(15)
- H(10)
- I(27)
- J
- K(4)
- L(9)
- M(16)
- N(6)
- O(13)
- P(36)
- Q
- R(14)
- S(45)
- T(23)
- U(5)
- V
- W(3)
- X
- Y(1)
- Z(1)
- 0(2)
Earth’s crust
Solid, outermost layer of the Earth, with an average depth of 35 – 40 km.
moreEast Wind Drift
Surface current in the Southern Ocean.
moreEcosystem
A system of mutually influencing living organisms and their physical environs. The definition of an ecosystem’s borders varies, depending on the respective research focus. Accordingly, the scale of ecosystems can range from very small to global.
moreEkman spiral
Ocean currents created by the Earth’s rotation and winds.
moreEl Niño
A naturally occurring climate phenomenon formed in the Pacific between the west coast of South America and east coast of Asia (Australia, Indonesia).
moreEM induction surveying
Electromagnetic induction surveying.
more
EM-Bird
The EM-Bird is a sensor used to determine the thickness of sea ice by helicopter or aeroplane
more
EMIC
Earth System Model of Intermediate Complexity.
moreEmissions
Release of substances, gases, etc. from natural or anthropogenic sources into the environment.
moreEmissions scenario
Emissions scenarios are potential future development paths for human emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols.
moreEmissions trajectories
Projections on future emissions paths or observed emissions patterns.
moreEmissivity
A given surface’s ability to emit energy, measured against a perfectly black body with 100% emissivity.
moreEndemic
Refers to species that are only found in naturally demarcated geographic regions.
moreEnergy
Energy is the ability to do work, produce heat or emit light. It describes the status of a body and is a conserved quantity. In a closed system, the total energy remains unchanged.
moreEnergy balance
The difference between total incoming energy and total outgoing energy.
more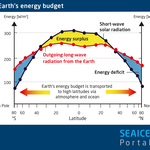
Energy efficiency
The relation between energy input and energy utilisation in a system, conversion process or activity.
moreENSO
Acronym for “El Niño – Southern Oscillation”, is a general term for the system of Pacific teleconnections produced by feedbacks between these two phenomena.
moreEnvironmental effectiveness
Describes the extent to which a given policy, measure or instrument achieves a specific, decisive or desired environmental effect.
moreEpiphytic
Organisms that live on plants but are not parasitic are epiphytic. Examples include algae, lichens and mosses.
moreEquivalent carbon dioxide (CO₂e) concentration
A unit of measurement used to compare the emissions of different greenhouse gases on the basis of their GWP (global warming potential).
moreErosion
The process of natural removal and transport of soil and rock in response to weathering and loss of mass due to the influence of waterways, glaciers, waves, wind and groundwater.
moreEulerian approach
Measuring sea ice in motion on the basis of a static system.
moreEuphausiacea
Bioluminescent crustaceans (krill) are marine crustaceans with naked gills. They are chiefly filter feeders and can emit light.
moreEuphausiacea superba
Krill.
more
Eutectic system
A substance in phase equilibrium
moreEvaporation
The transition of a liquid into a gas without reaching the boiling point.
moreExternal forces
External forces are forces from outside the climate system that cause changes in the system.
moreExtinction
When an entire species dies out worldwide.
moreExtracellular polymeric substances (EPSs)
EPSs are produced by various species of bacteria and cover the cell as a capsule. The capsule performs a wide range of functions, not all of which are fully understood.
moreExtreme weather event
An extreme weather event is one that rarely occurs at a given place and in a given season.
more