Glossary
The English version of our glossary is currently under construction and will be regularly updated.
- A(31)
- B(17)
- C(44)
- D(20)
- E(30)
- F(18)
- G(15)
- H(10)
- I(27)
- J
- K(4)
- L(9)
- M(16)
- N(6)
- O(13)
- P(36)
- Q
- R(14)
- S(45)
- T(23)
- U(5)
- V
- W(3)
- X
- Y(1)
- Z(1)
- 0(2)
dB
The decibel (dB) is the unit of measurement for loudness.
moreDecomposers
Microorganisms that break down other lifeforms’ organic excretions and the organic substances left behind when they die, converting them into simple inorganic compounds.
moreDeep water
Water masses at depths below ca. 1,000 m, which are formed by convection and overflow and spread from the convection areas to the interior ocean.
moreDeformed ice
General term for compressed ice.
more
Density anomaly
A density anomaly is a phenomenon in which a given substance’s density does not change with temperature or pressure in a linear manner. Instead, the density peaks at a certain temperature and/or pressure before declining again.
moreDetritus
Detritus refers to particulate material produced by the decomposition of dead plants and animals. In the context of water, it also includes suspended organic sediments.
moreDevelopment path
Describes a potential future climate and associated drivers. Development paths are also referred to as climate scenarios.
moreDiatoms
Microalgae.
more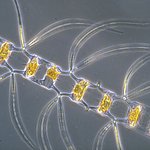
Dissipation
Transformation of one form of energy into another.
moreDissolved inorganic carbon (DIC)
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) refers to the total amount of dissolved inorganic carbon in water. It can be found in various carbonate species (bicarbonates, carbon dioxide and carbonates). The ratios of the various forms influence the pH value of the water and can reduce surface water’s ability to absorb CO2.
moreDissolved organic carbon (DOC)
DOC (dissolved organic carbon) generally refers to organic carbon compounds. A sum parameter, it is used to measure the total amount of dissolved, organic compounds. DOC particles are smaller than 0.45 µm in diameter.
moreDiurnal variation
Refers to changes in a given parameter in the course of the day.
moreDivergence
This term is used to describe a type of sea-ice motion in which the ice generally drifts apart.
moreDiverging / loosening up of drifting ice or ice fields
Due to divergent motion, the ice concentration is reduced, causing any tension in the ice to subside.
moreDownscaling
Mathematical technique used to apply the projections in global climate models to the regional scale.
moreDraft
The distance between the underside of sea ice and the ocean’s surface.
more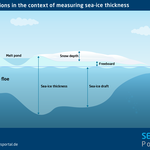
Drifting ice
A term used to broadly describe an area covered by sea ice, regardless of the type or distribution – except for fast ice and new ice. Examples include ice floes formed when grease ice or slush freezes in a choppy sea, or when sheets of new ice break up.
moreDrifting ice
Ice on rivers, lakes or seas that moves in response to wind, currents or other forces.
moreDrought
Drought refers to a lack of water, most often caused by insufficient precipitation and / or increased evaporation due to higher temperatures (or wind).
moreDynamic regional models
Dynamic regional models “reconstruct” Earth’s climate system on the basis of physically describable relations.
more